Delta Lake

Delta and Databricks
Delta Lake is an open-source storage framework that enables building a Lakehouse architecture with compute engines including Spark, PrestoDB, Flink, Trino, and Hive and APIs for Scala, Java, Rust, Ruby, and Python.
Databricks originally developed the Delta Lake protocol and continues to actively contribute to the open source project. Many of the optimizations and products in the Databricks Lakehouse Platform build upon the guarantees provided by Apache Spark and Delta Lake.
Main features:
- ACID transactions
| Atomicity | Consistency | Isolation | Durability |
|---|---|---|---|
| All or nothing | Data is always valid | Concurrent reads and writes | Data is always available |
| Commit or rollback | Types, PK | Read committed / uncommitted | Persisted to disk |
- Schema enforcement
- Schema evolution
- Time travel
- Audit history
- Upserts / Merge
- Deletes
- Streaming
- Change Data Feed
Apache Parquet
Apache Parquet is an open source, column-oriented data file format designed for efficient data storage and retrieval.
Delta Concept
TIP
- Delta is NOT a file format
- Delta uses PARQUET as file format.
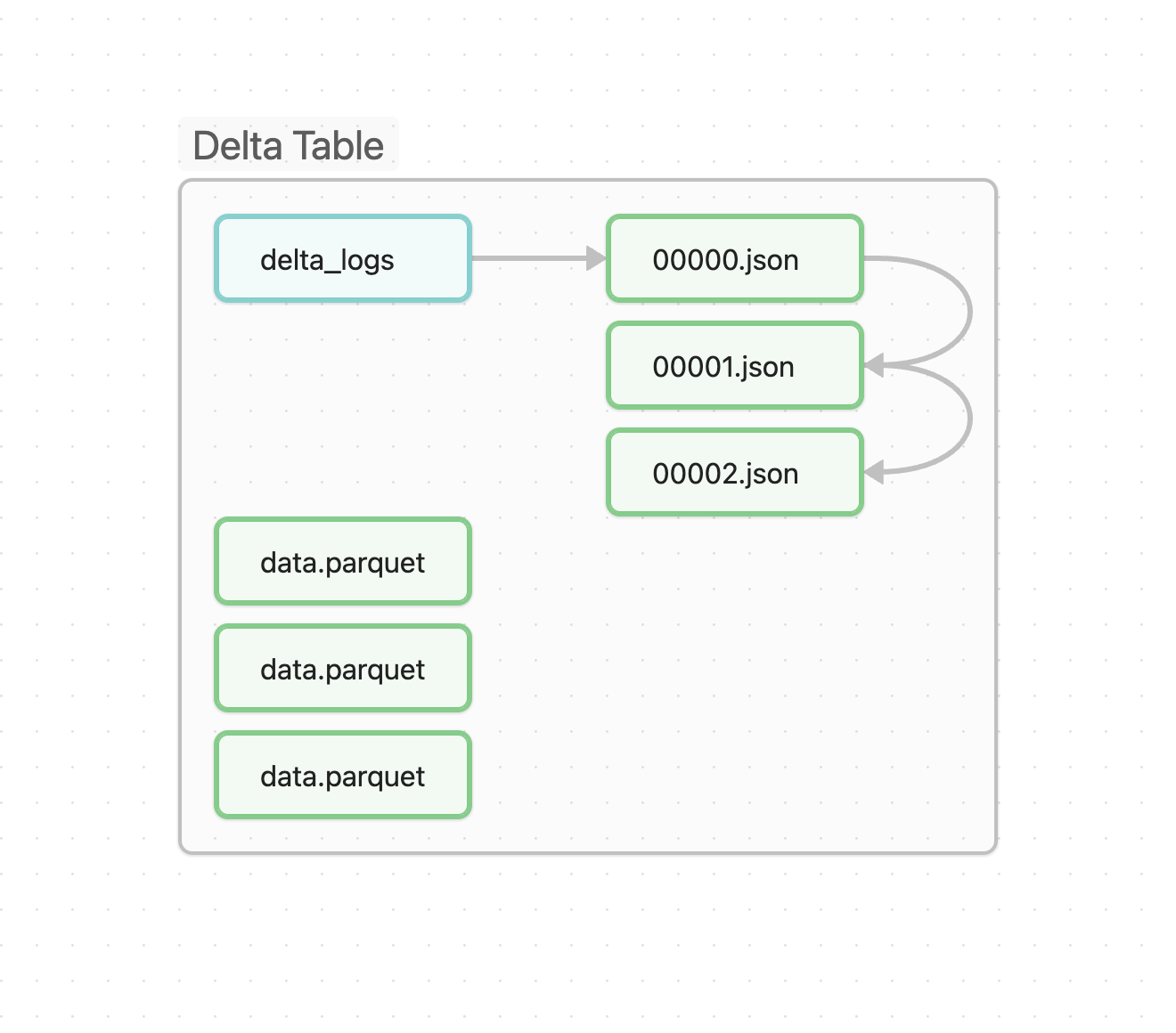
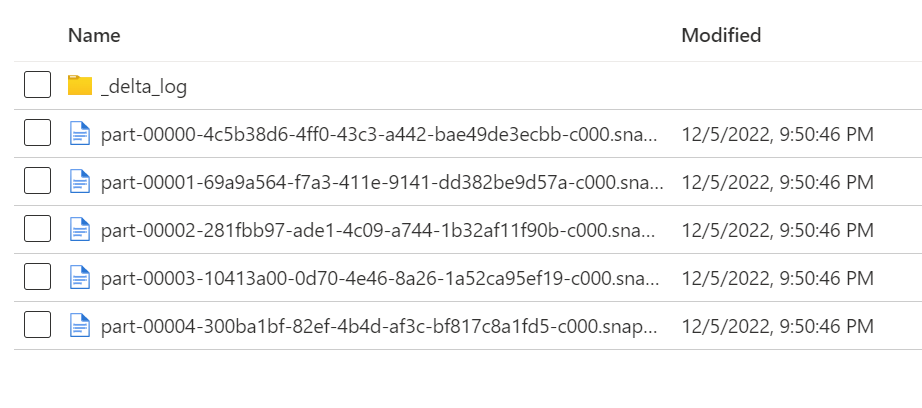
_delta_log is a folder that contains the transaction log of all the changes made to the table.
- 00001.json is the first version of the table.
- 00002.json is the second version of the table.
- and so on...
How to use Delta
In order to use all Delta features, you probably want to use Spark, but you can also use Delta without it.
TIP
It"s possible to use Delta without Spark, but not all features are available.
See Delta-Rs for example.
Local Spark
You can use the Spark Quickstart to get a local Spark cluster running.
Delta Versions
WARNING
You must match the Delta version with the Spark version.
See Delta Versions for more information.
Usage with PySpark
Install:
poetry add delta-sparkYou can import Delta Lake using the following code:
from pyspark.sql import SparkSession
from delta import *
spark = (
SparkSession
.builder
.master("local[*]")
.config("spark.jars.packages", "io.delta:delta-core_2.12:2.1.0")
.config("spark.sql.extensions", "io.delta.sql.DeltaSparkSessionExtension")
.config("spark.sql.catalog.spark_catalog", "org.apache.spark.sql.delta.catalog.DeltaCatalog")
.getOrCreate()
)Basic Operations
Check if delta exists
DeltaTable.isDeltaTable(spark, "path/table")
#True or FalseCreate
(
df
.write
.format("delta")
.mode("append")
.partitionBy("column")
.save("path/table")
)Create if not exists
TIP
if merging data, you must create the table first, otherwise you will get an error.
(
DeltaTable
.createIfNotExists(spark)
.tableName(table_name)
.addColumns(df.schema)
.location(path)
.execute()
)Merge / Upsert
WARNING
When using merge ALWAYS make sure you have no duplicates on the dataset you will use.
(
delta_table.alias("destination")
.merge(
dataframe.alias("updates"),
"destination.pk = updates.pk"
)
.whenMatchedUpdateAll()
.whenNotMatchedInsertAll()
.execute()
)Update
(
delta_table.alias("destination")
.merge(
dataframe.alias("updates"),
"destination.pk = updates.pk"
)
.whenMatchedUpdate(
set={ "col": "value" }
)
.execute()
)Insert
Just specific columns
(
delta_table.alias("destination")
.merge(
dataframe.alias("updates"),
"destination.pk = updates.pk"
)
.whenNotMatchedInsert(
values = {
"target.key": "source.key",
"target.lastSeen": "source.timestamp",
"target.status": "'active'"
}
)
.execute()
)Delete
Deleting data where column has value 1
delta_table.delete(" col = 1 ")Deleting rows where pks that doesn't exists in the new dataframe (updates)
(
delta_table.alias("destination")
.merge(
dataframe.alias("updates"),
"destination.pk = updates.pk"
)
.whenNotMatchedBySourceDelete()
.execute()
)Change Data Feed
CDC, but for Delta Tables.
Config
CREATE TABLE student
(id INT, name STRING, age INT)
TBLPROPERTIES (delta.enableChangeDataFeed = true)
-- or
ALTER TABLE myDeltaTable
SET TBLPROPERTIES (delta.enableChangeDataFeed = true)Or in spark session
builder = (
SparkSession.builder.appName("DeltaLakeApp")
.config("spark.jars.packages","io.delta:delta-core_2.12:2.4.0")
.config("spark.sql.extensions", "io.delta.sql.DeltaSparkSessionExtension")
.config("spark.sql.catalog.spark_catalog", "org.apache.spark.sql.delta.catalog.DeltaCatalog")
.config("spark.databricks.delta.properties.defaults.enableChangeDataFeed", "True")
)
spark = configure_spark_with_delta_pip(builder).getOrCreate()Usage
# version as ints or longs
(
spark
.read
.format("delta")
.option("readChangeFeed", "true")
.option("startingVersion", 0)
.option("endingVersion", 10)
.load("pathToMyDeltaTable")
)
# timestamps as formatted timestamp
(
spark
.read
.format("delta")
.option("readChangeFeed", "true")
.option("startingTimestamp", "2021-04-21 05:45:46")
.option("endingTimestamp", "2021-05-21 12:00:00")
.load("pathToMyDeltaTable")
)
# providing only the startingVersion/timestamp
(
spark
.read
.format("delta")
.option("readChangeFeed", "true")
.option("startingVersion", 0)
.load("pathToMyDeltaTable")
)Optimize
Small files are a common problem in data lakes. They can cause performance issues and increase costs.
from delta.tables import *
deltaTable = DeltaTable.forPath(spark, pathToTable)
deltaTable.optimize().executeCompaction()If you have a large amount of data and only want to optimize a subset of it, you can specify an optional partition predicate using where
deltaTable.optimize().executeCompaction()Control the size of the files using:
# 128 mb
.config("spark.databricks.delta.optimize.maxFileSize", 134217728)