Init
The follwing code provides the installation of packages avro and delta. If you do not need them, you can remove them.
# Import SparkSession
from pyspark.sql import SparkSession
# Create SparkSession
spark = (
SparkSession
.builder
.master("local[*]")
.config("spark.jars.packages", "org.apache.spark:spark-avro_2.12:3.3.1")
.config("spark.jars.packages", "io.delta:delta-core_2.12:2.1.0")
.config("spark.sql.extensions", "io.delta.sql.DeltaSparkSessionExtension")
.config("spark.sql.catalog.spark_catalog", "org.apache.spark.sql.delta.catalog.DeltaCatalog")
.getOrCreate()
)Read
CSV
df_csv = ( spark
.read
.option('delimiter', ';')
.option('header', 'true')
.option('inferSchema', 'true')
.option('encoding', 'ISO-8859-1')
.csv('data/filename.csv')
)JSON
df_json = (
spark
.read
.json('data/filename.json')
)Parquet
df_parquet = (
spark
.read
.parquet('data/parquet/')
)Delta
df_delta = (
spark
.read
.format('delta')
.load('data/delta/')
)Avro
# avro schema
schema = open('./data/avro/userdata.avsc', 'r').read()
df_avro = (
spark
.read
.format('avro')
.option('avroSchema', schema)
.load('data/avro/*')
)ORC
df_orc = (
spark
.read
.orc('./data/orc/')
)JDBC
Simple JDBC:
Import Table
(
spark
.read
.format("jdbc")
.option("url", "<jdbc-url>")
.option("dbtable", "<table-name>")
.option("user", "<username>")
.option("password", "<password>")
.load()
)Execute Query
(
spark
.read
.format("jdbc")
.option("url", "<jdbc-url>")
.option("query", "select c1, c2 from t1")
.option("user", "<username>")
.option("password", "<password>")
.load()
)Complex JDBC:
By default, Spark will store the data read from the JDBC connection in a single partition. As a consequence, only one executor in the cluster is used for the reading process. To increase the number of nodes reading in parallel, the data needs to be partitioned by passing all of the following four options:
partitioningColumndetermines which table column will be used to split the data into partitions. The data type of partitioning column needs to beNUMERIC,DATEorTIMESTAMP.numPartitionssets the desired number of partitions.lowerBoundandupperBoundare used to calculate the partition boundaries.
Under the hood, Spark will generate a SQL query for each partition with an individual filter on the partitioning column. The diagram below illustrates how data is divided into four partitions using the options above:
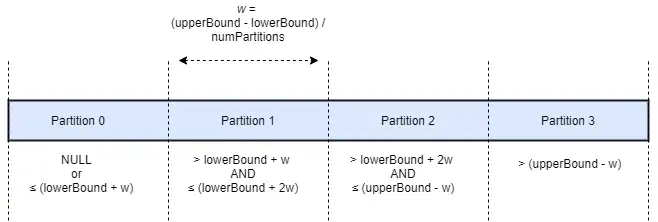
Partitioning example:
Change COLUMN_NAME and TABLE_NAME to your values.
query_min_max = f"""
SELECT Min(COLUMN_NAME),
Max(COLUMN_NAME)
FROM TABLE_NAME s
"""
# Determine min and maximum values
df_min_max = spark.read.jdbc(
url="jdbc:postgresql://db/postgres",
table=f"({query_min_max}) t ",
properties=connection_properties,
).collect()
min, max = df_min_max[0][0], df_min_max[0][1]
query = """
SELECT category, value
FROM TABLE_NAME
"""
# Partition the data
df = (
spark
.read
.option("numPartitions", 30)
.option("partitionColumn", "category")
.option("lowerBound", min)
.option("upperBound", max)
.jdbc(
url="jdbc:postgresql://db/postgres",
table=f"({query}) t ",
properties=connection_properties,
)
)Partition on String Column
with cte as (
select abs(mod(hashtext("COLUMN"),5)) as partition_group,
*
from people
)
select count(partition_group), partition_group
from cte
group by partition_group
order by 2Result on 2 milion rows and 5 partitions:
| count | partition_group |
|---|---|
| 400535 | 0 |
| 399090 | 1 |
| 400691 | 2 |
| 400376 | 3 |
| 399308 | 4 |
Schema
TIP
Work in progress
Useful Functions
# Show schema
dataframe.printSchema()
# Show first rows
# arg1 - number of rows
# arg2 - truncate column values
# arg3 - show dataframe in vertical orientation
dataframe.show(20, truncate=False, vertical=True)
# Number of rows
dataframe.count()
# Number of columns
len(dataframe.columns)
# Select columns
dataframe.select('column_name', 'column_name2')Drop Columns
drop_cols = ("COL1", "COL2")
df.drop(*drop_cols)Join
# Join two dataframes
(
table1.alias("one")
.join(
table2.alias("two"),
[
F.col("one.user_id") == F.col("two.user_id"),
F.col("one.company_id") == F.col("two.company_id"),
],
"inner"
)
.show(5)
)Aggregations
TIP
Work in progress
SparkSQL
How to run SQL queries on spark dataframes:
# Create or replace view to use SQL
dataframe.createOrReplaceTempView('dataframe')
# Spark SQL Example
spark.sql("""
SELECT COLUMN_NAME,
COLUMN_NAME2
FROM dataframe
LIMIT 5
""").show()
# Drop view after usage
spark.catalog.dropTempView('dataframe')Window Functions
from pyspark.sql.window import Window
from pyspark.sql import functions as F
windowSpec = (
Window
.partitionBy("user_id","company_id")
.orderBy("user_id","company_id")
)
(
table1
.withColumn(
"row_number",
F.row_number().over(windowSpec)
)
.show()
)Save
Csv
(
df_csv
.write
.mode('overwrite')
.option('sep', ';')
.option('header', 'true')
.option('encoding', 'ISO-8859-1')
.csv('data/csv/')
)Json
(
df_json.write
.partitionBy('color')
.mode('overwrite')
.json('data/path/')
)Parquet
(
df_parquet
.write
.mode('overwrite')
.parquet('data/path/dataframe.parquet')
)Delta
(
df_delta
.write
.format("delta")
.mode('overwrite')
.save("/data/path/")
)Avro
(
df_avro
.write
.mode('overwrite')
.format('avro')
.save('data/path/')
)Orc
(
df_orc
.write
.partitionBy('_col5')
.mode('overwrite')
.orc('data/path/')
)UDF
User defined functions can be used to apply custom functions to dataframes.
Example: Apply 10% discount to all products orders after the third order of each customer.
from pyspark.sql import functions as F
from pyspark.sql.window import Window
windowSpec = Window.partitionBy("COLUMN1").orderBy("COLUMN1","COLUMN3")
def calc_discount():
return F.when(F.col("row_number") > 3, F.col("value") * 0.90 ).otherwise(F.col("value"))
udf_discount = F.udf(lambda z: calc_discount)
orders_with_discount = (
orders
.join(products,["COLUMN2"],"inner")
.withColumn("row_number", F.row_number().over(windowSpec))
.withColumn("value_with_discount", calc_discount())
)
orders_with_discount.show(truncate=False)Drop Duplicates
WARNING
Be careful when using .DropDuplicates() as it won't work on multiple partitions.
It will only drop duplicates within a partition.
from pyspark.sql import Window
from pyspark.sql.functions import rank, col, monotonically_increasing_id
window = Window.partitionBy("DESIRED_COLUMN").orderBy('tiebreak')
(
df_s
.withColumn('tiebreak', monotonically_increasing_id())
.withColumn('rank', rank().over(window))
.filter(col('rank') == 1)
.show()
)Check if DF is empty
df.head(1).isEmpty